Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
What is TMS Therapy?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a safe, effective, nonpharmacological treatment to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. With over 20 years of research, the FDA approved TMS Therapy in 2008 for treatment for Adults with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) who have failed to achieve satisfactory improvement from previous antidepressants and other therapies.
How does TMS Therapy work?
Repetitive magnetic pulses non-invasively penetrate through the skull and into the cortex stimulating nerve cells in the brain that are found to be underactive in patients with Depression. The magnetic pulses induce tiny electrical charges that can cause the nerve cells to increase their level of activity. When a certain threshold of increased activity of the nerve cells is achieved, then outward signs of mood improve, with higher energy levels and a sense of well being.
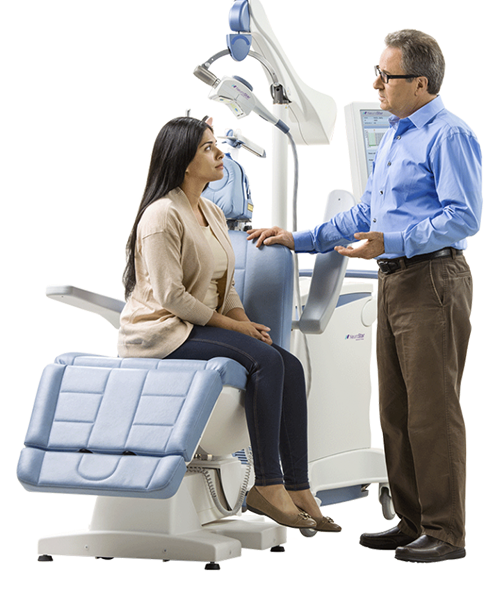
What is Neuronavigated TMS?
At Smart Brain and Health, we utilize Neuronavigation to precisely target the location of the brain for TMS Therapy. Neuronavigation is a computer-based tool that is used in conjunction with fMRI (Functional MRI) images that enables our physicians to pinpoint the exact area in the brain responsible for the patient’s diagnosis (Depression, Anxiety, OCD, and additional pathologies). We utilize a system called Brainlab, which was pioneered for brain surgeons, to ensure our patients are receiving the most effective form of TMS Therapy here at Smart Brain and Health. In short, Neuronavigation is our “GPS for the Brain.”™
What is Theta Burst TMS?
At Smart Brain and Health, our team of physicians and specialists are constantly working on the most advanced techniques to improve patients’ overall experience. In addition to our Standard TMS, we also Theta Burst TMS, also known as TBS.
While Standard TMS employs 10 Hz (the number of hertz equals the number of cycles per second) magnetic frequency for 20-40 minutes, TBS uses 50 Hz magnetic frequency for just three minutes! TBS sends three rapid bursts every fraction of a second, mimicking the brain’s neuronal pattern of firing theta waves.
A large number of people who suffer from Depression, including medication resistant depression (MRD), experience impaired cognitive function both during and after depressive episodes. A 2015 study published in Progress in Neuro- Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry showed that intermittent TBS is an effective method for improving executive function in patients with and without depression.

How is TMS treatment different from other treatments?
TMS Therapy treats the source of the problem - for patients with Depression, we treat the underactive neurons in your brain, and for patients with Anxiety/OCD, we treat the hyperactive neurons.
Medications can be directed at a specific neurochemical receptor or protein, however because they are ingested orally the chemicals can circulate throughout the body and can affect any tissue of the body regardless of the disease being treated and can cause systemic side effects.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT or “Shock Therapy”) patients must be driven to an outpatient hospital setting and the patient must be restained and/or sedated. Electrical stimulation can induce seizures, cognitive impairment (i.e. memory loss, short-term confusion), and sore muscles.The application of anesthesia means it can take hours for a patient to recover and continue with their day.
TMS Therapy has little to no side effects; the only reported side effect, which has only been reported in some cases, is a slight headache which usually goes away after the first few treatments. In today’s fast-moving society, it’s important to be able to return to one’s daily routine immediately following medical treatment. With transcranial magnetic stimulation, all patients are able to return to their daily activities almost immediately.







